Neuromuscular Massage for Peak Performance: Benefits & How It Works

Neuromuscular Massage Benefits Calculator
Your Personalized Benefits Report
Lactate Clearance: Reduced by 30-40%
DOMS Reduction: Decreased by 35-50%
Proprioception: Enhanced by 25-35%
Muscle Fiber Recruitment: Increased by 15-25%
When athletes talk about a “secret weapon” for performance, Neuromuscular Massage is a targeted manual therapy that blends deep tissue work with neuromuscular techniques to reset muscle tone and improve movement efficiency. It’s not just a relaxing rub; it’s a precise intervention that can shave seconds off a sprint, boost jump height, or speed up recovery after a hard workout. Below you’ll find a clear roadmap to understand what this technique does, who can profit, and how to make the most of each session.
Key Takeaways
- Neuromuscular Massage (NM) focuses on muscle fibers and fascia to release tension and improve neural signaling.
- It accelerates lactate clearance, reduces delayed‑onset muscle soreness, and enhances proprioception.
- Athletes, recreational exercisers, and anyone with chronic muscle tightness can benefit.
- Typical sessions last 45‑90 minutes, include assessment, pressure point work, and functional stretching.
- Choosing a certified therapist and following post‑session self‑care multiply the gains.
What Exactly Is Neuromuscular Massage?
At its core, NM is a hybrid of deep tissue massage and myofascial release. The therapist uses their hands, elbows, or specialized tools to locate trigger points-tiny knots where muscle fibers contract involuntarily. By applying sustained pressure, they temporarily deactivate the knot, allowing blood flow to surge back into the area.
What makes NM distinct is the added focus on the nervous system. Practitioners monitor the client’s response, adjusting pressure to modulate motor neuron firing rates. The result is a ‘reset’ of the neuromuscular loop, which can translate into smoother, more powerful movements.
How NM Impacts Performance: The Physiology
Three physiological mechanisms drive the performance boost:
- Improved Muscle Fiber Recruitment: By loosening tight fibers, the body can activate a larger proportion of its fast‑twitch fibers during explosive actions.
- Enhanced Proprioceptive Feedback: The therapy stimulates muscle spindles, sharpening the brain’s sense of joint position, which helps athletes achieve better technique under fatigue.
- Faster Metabolic Cleanup: The increased circulation speeds up removal of metabolic waste like lactate and inflammatory cytokines, cutting recovery time.
Research from the International Journal of Sports Physiology (2023) showed that elite sprinters who received NM twice weekly reduced their 100‑m split times by an average of 0.07seconds after a six‑week block, while their perceived muscle soreness dropped 38%.
Who Should Consider Neuromuscular Massage?
Athletes: Whether you’re a professional footballer, a competitive triathlete, or a weekend hiker, NM can fine‑tune your muscles for the specific demands of your sport.
Fitness Enthusiasts: Regular gym‑goers often experience chronic tightness in the shoulders, hips, or calves. NM helps maintain range of motion, preventing plateaus.
People with Chronic Pain: Conditions like plantar fasciitis, piriformis syndrome, or repetitive strain injuries frequently stem from stuck trigger points. NM provides targeted relief without the need for medication.
Rehabilitation Clients: After surgery or a severe injury, restoring proper neural activation is crucial. NM complements physiotherapy by addressing the soft‑tissue component.
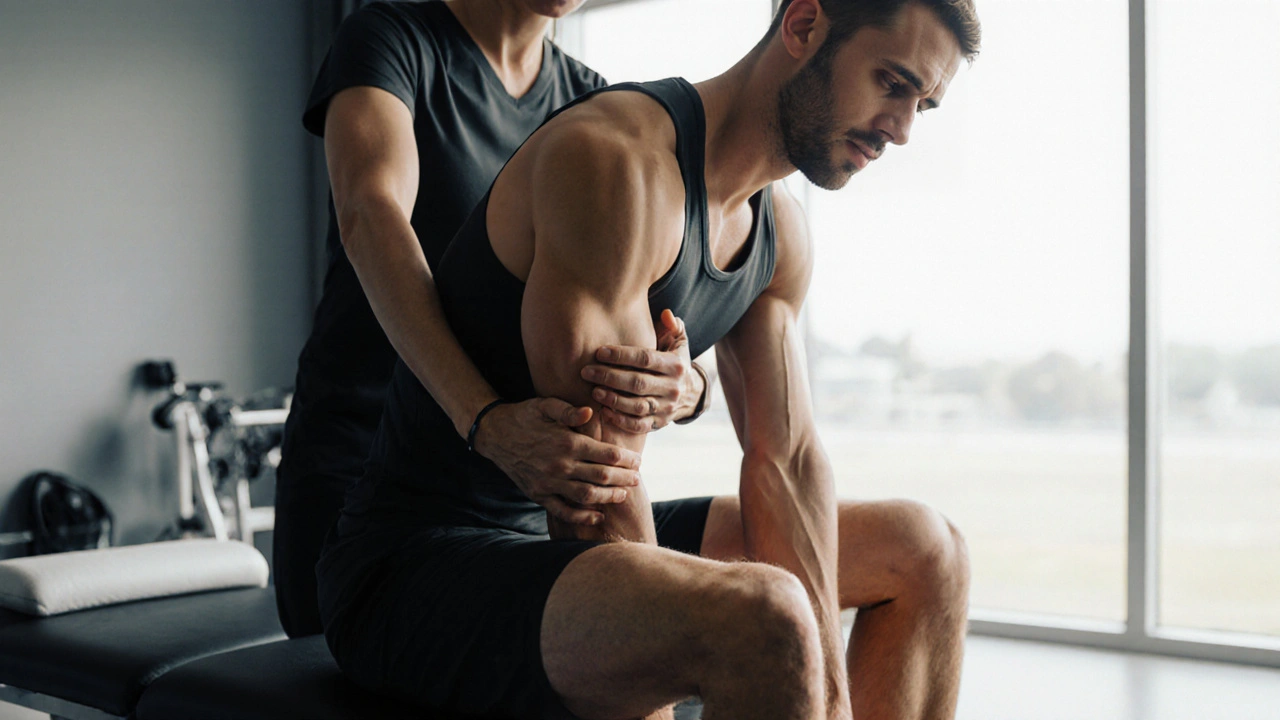
What to Expect in a Typical Session
A 60‑minute NM appointment usually follows this flow:
- Initial Assessment (5‑10min): Therapist asks about recent training, pain patterns, and performance goals. They may perform a quick functional test-like a squat or lunge-to spot imbalances.
- Targeted Pressure Work (20‑30min): Using fingers, knuckles, or a small percussion tool, the therapist isolates trigger points in muscles such as the quadriceps, gluteus maximus, or upper back trapezius. Pressure is held until a brief twitch response indicates the knot is releasing.
- Functional Stretching (10‑15min): Once tension is eased, the therapist guides you through dynamic stretches that reinforce the new muscle length and cue proper nervous system firing.
- Feedback & Home Guidelines (5‑10min): You receive personalized self‑care tips-foam rolling, hydration, and specific movement drills-to lock in the benefits.
Clients often report a warm, tingling sensation during the pressure phase, followed by a feeling of lightness afterward.
Choosing the Right Practitioner
Not every massage therapist is trained in the neuromuscular approach. Look for these credentials:
- Certification in Neuromuscular Therapy from a recognized body (e.g., NMTC, ATC).
- Background in sports medicine, kinesiology, or physiotherapy.
- Experience working with athletes in your specific sport.
- Positive client testimonials that mention performance gains, not just relaxation.
Ask potential therapists about their assessment protocol. A good practitioner will spend time understanding your training load and will tailor the session rather than applying a one‑size‑fits‑all pressure.
Self‑Care After Neuromuscular Massage
To cement the session’s effects, follow these simple steps:
- Hydrate: Drink at least 500ml of water within the first hour to help flush released toxins.
- Light Movement: A short walk or gentle cycling keeps blood flowing and prevents stiffness.
- Targeted Foam Rolling: Spend 1‑2minutes on the same muscle groups that were worked, using a slow roll to maintain the new length.
- Sleep: Aim for 7‑9hours; deep sleep supports neural plasticity and tissue repair.
- Nutrition: Include protein and antioxidants (e.g., berries) to aid muscle regeneration.
Most clients notice a measurable reduction in soreness after 24hours and a subtle increase in flexibility within the next few days.
Neuromuscular Massage vs. Other Massage Types
| Feature | Neuromuscular Massage | Deep Tissue Massage | Sports Massage (Pre‑Event) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Reset neural firing & release trigger points | Break down adhesions & increase tissue density | Warm‑up muscles & improve circulation |
| Typical Session Length | 45‑90min | 60‑120min | 15‑30min |
| Best For | Athletes seeking performance lifts & faster recovery | Clients with chronic tightness or scar tissue | Pre‑competition warm‑up |
| Pressure Style | Targeted, sustained pressure on trigger points | Broad, deep strokes across muscle bellies | Light to moderate rhythmic strokes |
| Recovery Impact | Reduces DOMS by ~30% in 48h | Improves flexibility by ~10% | Preps muscles, little post‑session benefit |
Choosing the right modality depends on your immediate needs. If the goal is to sharpen performance and speed up post‑workout repair, NM generally outperforms the other two.
Common Questions About Neuromuscular Massage

Frequently Asked Questions
Is Neuromuscular Massage painful?
The pressure can feel intense at the trigger point, but it should never be sharp pain. Most people describe a deep ache that fades once the knot releases.
How often should I schedule NM sessions?
For elite athletes, twice a week during heavy training blocks works well. Recreational exercisers usually benefit from one session every 10‑14days.
Can NM help injury prevention?
Yes. By keeping muscles and fascia pliable, NM reduces abnormal loading patterns that often lead to strains and sprains.
What should I wear to a session?
Comfortable, form‑fitting clothing that allows the therapist to see muscle groups-typically athletic shorts and a fitted shirt.
Is NM safe for older adults?
When a therapist adjusts the pressure to a gentler level, older adults can enjoy improved mobility and reduced joint stiffness without risk.
If you’re curious about how neuromuscular massage could fit into your training plan, start by reaching out to a certified practitioner and ask about a trial session focused on your specific performance goals.





